The ocean ridge rises to between 2 to 3 km above the ocean floor and has a rift valley at its crest marking the location at which the two plates are moving apart.
What causes the ocean floor to separate and grow.
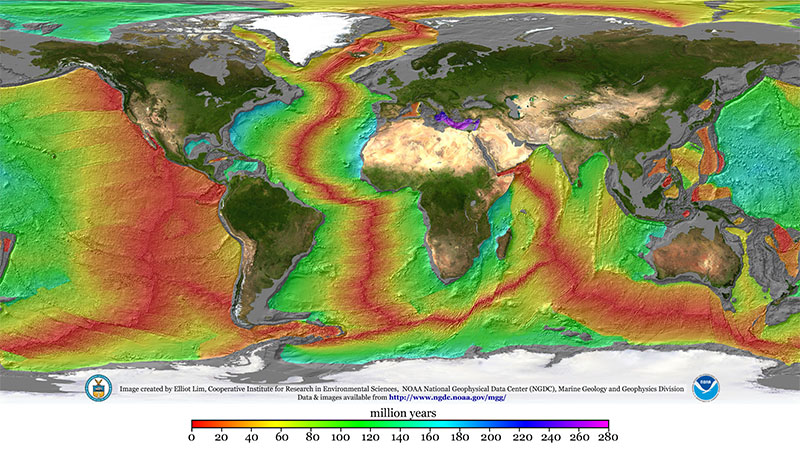
The ocean basins are relatively young.
They are also known as spreading centers or divergent plate boundaries.
While most life on this planet requires sunlight to live there is an.
This increase in temperature causes glaciers to melt and sea levels and temperatures to rise which causes different weather patterns and severe weather like hurricanes and changes the climate.
The mid atlantic ridge like other ocean ridge systems has developed as a consequence of the divergent motion between the eurasian and north american and african and south american.
This graphic shows several ocean floor features on a scale from 0 35 000 feet below sea level.
Seafloor spreading is a process that occurs at mid ocean ridges where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.
Continental shelf 300 feet continental slope 300 10 000 feet abyssal plain 10 000 feet abyssal hill 3 000 feet up from the abyssal plain seamount 6 000 feet.
A transform plate boundary is characterized by.
Mid ocean ridges cause the ocean floor to separate and grow.
The magnetism of mid ocean ridges helped scientists first identify the process of seafloor spreading in the early 20th century.
Most ocean basin rocks and sediments are cretaceous or younger in age.
Back in 1977 a very interesting discovery was made on the deep ocean floor where no light penetrates.
Mid ocean ridges circle the earth like the seams on a giant baseball.
The following features are shown at example depths to scale though each feature has a considerable range at which it may occur.
The magma that rises from below these ridges lifts the ocean floor.
The sea floor is spreading from some areas but is shrinking in others.
Climate change affects marine primary productivity as the increased temperatures and amounts of sunlight result in a lower level of productivity.